Table of Contents
Stainless steel sheet bending is a process that uses bending machines and other equipment to apply pressure to stainless steel plates to cause them to undergo plastic deformation along certain lines and eventually form the desired angle and shape. Due to the material properties of stainless steel, its bending process is somewhat more special and challenging than that of ordinary steel.
1. Analysis of the characteristics of stainless steel

Stainless steel is an alloy steel with excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties. It is widely used in construction, industry, home, medical and other fields due to its smooth surface, high strength and long service life. The following are the main characteristics of stainless steel.
1) Corrosion resistance
Core features:
Stainless steel contains a certain proportion of chromium (usually ≥10.5%), and a dense chromium oxide protective film (passivation film) is formed on the surface, which can effectively prevent corrosion.
Application scenarios:
Suitable for corrosive environments such as moisture, acidity, alkalinity, and salt spray, such as marine equipment, chemical equipment, etc.
Influencing factors:
The higher the content of elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum in stainless steel, the stronger the corrosion resistance.
In special occasions (such as high chloride environments), higher grades of stainless steel (such as 316L) need to be selected.
2) Excellent mechanical properties
High strength:
Stainless steel has high yield strength and tensile strength and can withstand large loads.
Good ductility:
High elongation, suitable for deep drawing, bending and other processing processes.
High toughness:
Even under low temperature conditions, it can still maintain good toughness and strength.
3) High temperature and low temperature resistance
High temperature resistance:
Some stainless steels (such as 304, 310S) can maintain good strength and oxidation resistance under high temperature environments.
Low temperature resistance:
Austenitic stainless steel (such as 304, 316) will not undergo brittle fracture at low temperatures and is suitable for extremely low temperature environments such as liquid nitrogen and liquid hydrogen.
4) Excellent processing performance
Easy to form:
Stainless steel has good ductility and is suitable for processing processes such as stamping, stretching, and bending.
Weldability:
Most stainless steels have good welding performance and are suitable for a variety of welding methods (such as TIG welding, MIG welding, laser welding, etc.).
Easy to cut:
Some stainless steels (such as 303) are optimized and designed to improve cutting performance.
5) Aesthetics
Surface finish:
The surface of stainless steel is smooth and bright, and it is more decorative after polishing, brushing, sandblasting, etc.
Diverse surface treatments:
Mirror, matte, brushed, color coating and other effects can be achieved to meet different design requirements.
6) Durability
Long life:
Stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, and can maintain a long service life in harsh environments.
Low maintenance:
Stainless steel is not easy to rust or corrode, reducing maintenance costs.
7) Environmental protection and recyclability
Environmentally friendly materials:
Stainless steel is harmless to the human body and is often used in food, medical equipment and other fields.
Recyclable:
Stainless steel can be 100% recycled, which is in line with the concept of sustainable development.
2. Characteristics of stainless steel sheet bending
Stainless steel sheet bending is a processing technology that uses mechanical force to plastically deform stainless steel sheets. It is widely used in the manufacture of various metal products and parts. Due to the unique physical and chemical properties of stainless steel, its bending process also has the following significant characteristics.
1) High strength and high hardness
– Features:
Stainless steel has high yield strength and hardness, and requires greater pressure than ordinary carbon steel when bending.
– Influence:
Bending equipment needs to have a higher tonnage, and mold materials need to be wear-resistant.
2) Large rebound
– Features:
Stainless steel has a high elastic modulus and is prone to rebound after bending, causing the actual angle to deviate from the designed angle.
– Coping methods:
Compensate for rebound by increasing the bending angle.
Use special molds or clamping devices to reduce rebound.
3) Good ductility
– Features:
Stainless steel has high ductility and can be bent at a larger angle without breaking easily.
– Advantages:
Suitable for processing complex shapes and multiple bends.
4) Surface scratches
– Features:
The surface of stainless steel is smooth, but it is easy to be scratched or pressed by the mold during the bending process.
– Solution:
Use soft materials (such as polyurethane pads) on the mold to protect the surface.
Apply a protective film to the stainless steel surface.
5) Processing difficulty is proportional to thickness
– Features:
The thicker the stainless steel plate, the more difficult it is to bend, requiring greater bending force and higher equipment performance.
– Suggestions:
For thick plates, choose a large-tonnage bending machine.
Select the bending radius reasonably to avoid cracking caused by excessive deformation.
6) Strict requirements on bending radius
– Features:
Too small a bending radius may cause cracking on the stainless steel surface or internal stress concentration.
– Recommendation:
The bending radius should be 1-3 times the thickness of the plate, depending on the material properties.
Special uses require experimental verification of the optimal radius.
7) Poor thermal conductivity
– Features:
Stainless steel has poor thermal conductivity, and heat is not easy to dissipate during bending, which may cause local deformation.
– Response:
Use a cooling system or intermittent processing to avoid heat accumulation.
8) Processing direction affects bending quality
– Features:
Stainless steel has good ductility along the rolling direction and is prone to cracking when bent perpendicular to the rolling direction.
– Suggestion:
Bend along the rolling direction as much as possible.
For special-shaped bending parts, the processing direction can be adjusted through experiments.
9) High mold requirements
– Features:
The high hardness and high strength of stainless steel put forward higher requirements on the wear resistance and strength of the mold.
– Solution:
Use high-strength alloy steel molds.
Regularly check and maintain the mold to ensure a smooth and intact surface.
10) Tempering or work hardening effect
– Features:
Stainless steel may undergo work hardening during the bending process, increasing the difficulty of subsequent processing.
– Solution:
For materials with severe work hardening, tempering treatment is performed to eliminate stress.
Use the step-by-step bending method to reduce the amount of one-time deformation.
Stainless steel sheet bending has the characteristics of high strength, high rebound, and easy scratching due to its material characteristics, but through the reasonable selection of equipment, molds and process parameters, high-precision and high-quality processing effects can be achieved.
In actual production, fully understanding the characteristics of stainless steel and optimizing the process flow are the key to ensuring bending quality.
3. Stainless steel bending equipment and tools
1) Bending equipment
– Hydraulic press brake
Features: Provide high pressure through the hydraulic system, suitable for processing thick plates and large-sized stainless steel parts.
Advantages: High pressure, stable operation, high processing accuracy.
Application: Widely used in industrial equipment, heavy machinery parts processing.
– CNC press brake
Features: Automatically control the bending angle, pressure and position through the CNC system, suitable for high-precision and diversified processing.
Advantages: High efficiency, high repetition accuracy, support for complex parts bending.
Application: Suitable for high-end manufacturing industries such as aerospace and automotive industries.
– Mechanical bending machine
Features: Rely on mechanical transmission to provide bending force, suitable for processing thin plates and small parts.
Advantages: Simple structure and low cost.
Application: Suitable for ordinary processing needs of small and medium-sized enterprises.
– Manual bending machine
Features: Simple structure, relying on manual operation to complete bending, suitable for small batch production or maintenance work.
Advantages: Economical and flexible operation.
Application: Suitable for processing small parts or simple bending parts.

2) Bending tools
– Bending mold
Upper mold (punch):
Used to apply downward pressure to determine the bending angle and shape.
Common types: V-type mold, knife-type mold, arc mold, etc.
Lower mold (concave mold):
Used to support the workpiece and provide the bending shape.
Common types: single V-type mold, multi-V-type mold, U-type mold, etc.
Mold material:
High-strength alloy steel: wear-resistant, suitable for processing high-hardness stainless steel.
Surface treatment: The mold needs to be polished or plated to avoid scratching the stainless steel surface.
– Bending follower
Bending follower is an advanced technology used in stainless steel sheet bending. Its purpose is to follow the deformation of the sheet in real time through the follow-up device, provide support and assistance, reduce the deformation problem of the sheet during the bending process, and improve processing accuracy and efficiency. This technology is commonly used in high-end CNC press brake machines, especially for processing large-size or high-precision workpieces.
– Auxiliary tools
Protective gasket:
Used to prevent direct contact between the mold and stainless steel during the bending process to avoid surface scratches.
Common materials: polyurethane gasket, nylon gasket.
Pressing plate or clamp:
Used to fix stainless steel sheets to ensure stability and precision during processing.
Anti-scratch film:
Affixed to the stainless steel surface before bending to prevent scratches during bending.
3) Maintenance of equipment and tools
– Equipment maintenance
Check the hydraulic system regularly to ensure that there is no oil leakage and the pressure is stable.
Clean the surface of the equipment to prevent dust and oil from affecting the accuracy.
– Mold maintenance
The mold surface must be kept smooth and burr-free, and polished or replaced regularly.
Apply anti-rust oil during storage to avoid moisture and rust.
– Auxiliary tool maintenance
Protective gaskets or anti-scratch films need to be replaced regularly to avoid failure due to wear.
4) Improvement trend of stainless steel bending machines and tools
– Intelligence and automation
CNC bending machines are gradually becoming intelligent, improving processing efficiency and precision.
– High wear-resistant mold development
Mold materials are constantly upgraded to extend service life and reduce replacement frequency.
– Environmental protection and energy-saving design
New hydraulic systems and drive technologies reduce energy consumption and reduce environmental impact.
4. Key points for selecting stainless steel sheet bending equipment and tools
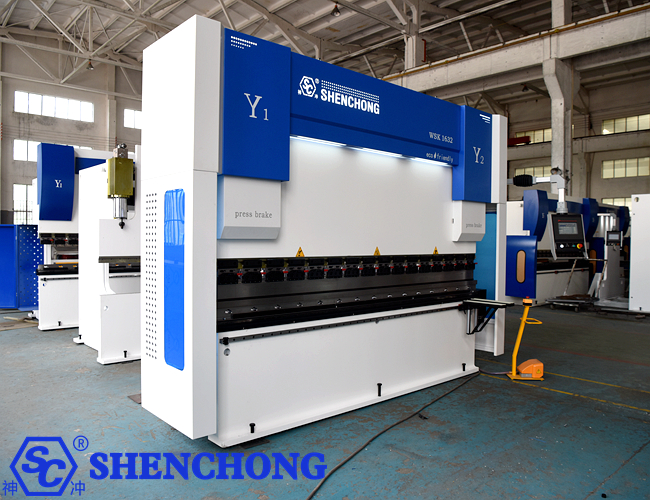

The selection of stainless steel bending equipment and tools is the key to ensuring processing quality and efficiency. Due to the high strength, high hardness and unique ductility of stainless steel, the selection of equipment and tools needs to be combined with plate characteristics, processing requirements and process parameters. The following are the main points of selection.
1) Select equipment tonnage according to plate thickness
The pressure (tonnage) of the bending machine needs to meet the processing requirements of plate thickness and length.
2) Select mold according to bending radius
The bending radius is related to the plate thickness, and the mold slot width is usually 8-10 times the plate thickness.
3) Select mold type according to bending angle
Small angle bending: sharp V-shaped molds are required.
Large angle bending or arc bending: arc molds or multiple bending processes are selected.
4) Select equipment type according to processing accuracy
High precision requirements: CNC hydraulic press brake machines are recommended.
Ordinary precision requirements: hydraulic or mechanical bending machines can be selected.
By selecting appropriate equipment and tools, combined with optimized process flow, the efficiency and quality of stainless steel bending processing can be effectively improved to meet various application requirements.
5. Precautions for stainless steel bending
Matching material thickness with equipment capacity
Choose the appropriate bending machine tonnage according to the thickness of stainless steel to avoid bending failure due to insufficient pressure.
Prevent surface scratches
Check whether the mold surface is smooth and burr-free before processing.
Use protective film or soften the mold surface.
Multiple bending control
For bending with large angles or complex shapes, multiple step-by-step bending methods can be used to avoid material cracking or deformation.
Processing direction
Try to bend along the rolling direction of stainless steel to reduce the risk of cracking.
Post-bending treatment
If surface scratches occur, they can be repaired by polishing or wire drawing.
For bent parts with welding requirements, ensure that there is no stress concentration in the bending area.
6. Conclusion
Due to its material properties, stainless steel sheet bending has the characteristics of high strength, high rebound, and easy scratching. In actual production, fully understanding the characteristics of stainless steel and optimizing the process flow are the key to ensuring the quality of bending.
By selecting appropriate equipment and tools, combined with optimized process flow, the efficiency and quality of stainless steel bending processing can be effectively improved to meet various application requirements.
Other related articles about sheet bending:
Common Bending Quality Problems And Solutions