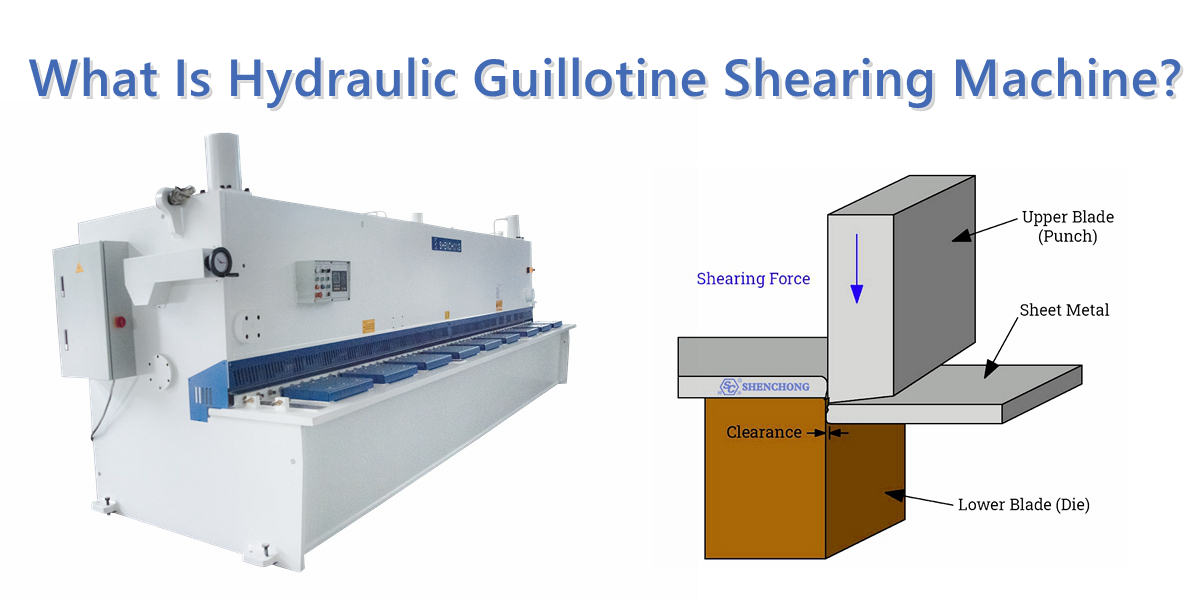
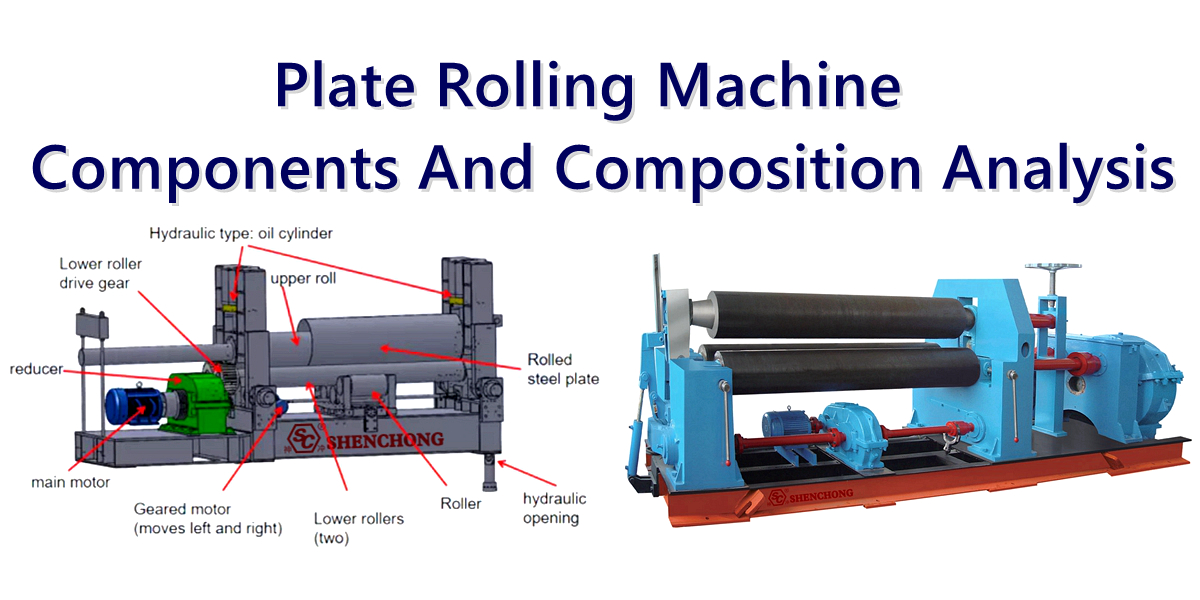
Punching machine is an important tool in the metal processing industry, used for forming, cutting, and shaping metal sheets or coils. This punching machine introduction article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of punching machines, covering their uses, applications, industries that use them, products manufactured, evolutionary history, processes, advantages and disadvantages, as well as factors to consider when choosing an ideal plate punching machine manufacturer. In addition, this punching machine introduction article conducts in-depth research on various types of punch presses, including mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, servo driven, and progressive punch presses and introduces a terminology list related to plate punching machine for better understanding.
Table of Contents
Punching Machine Introduction
The Evolution History Of Punching Machines
The history of punching machines can be traced back to the early stages of industrialization, when manual presses were used for basic metal forming tasks. Over time, mechanical plate punching machines driven by steam engines have completely changed the metal processing industry. In the 20th century, hydraulic and pneumatic punch machines improved accuracy and efficiency. Nowadays, computer numerical control (CNC) and servo driven punching machines can achieve high-speed and complex operations with extremely high precision.
What is Punching Machine Working Principle?
Punching machine introduction: Punching machine is a mechanical processing equipment mainly used for cold stamping, bending, stretching, shearing and other processes of metal materials. Compared to other mechanical equipment, punch machines have the advantages of fast processing speed, high processing accuracy, and fast one-time molding. The application fields of punching machines are very wide, including the manufacturing of various metal parts, automobiles, electronics, home appliances, instruments, etc.
The working principle of a punch machine is to use hydraulic or pneumatic power to apply pressure to the material, causing it to deform or separate, thereby manufacturing various shapes and sizes of parts or products. During the punching process of a plate punching machine, the material will gradually deform and be processed into the desired shape and size through a series of molds and cutting tools.
During the punching process, the operator places the metal sheet on the worktable of the mold, and then performs plastic deformation on the metal sheet through the downward movement of the mold. The working process of a punch press usually includes steps such as feeding, downward punching, discharging, and upward punching, each of which is precisely controlled and coordinated to ensure the accuracy and efficiency of the punching process.
Application Of Punching Machines
Sheet metal punching machines are widely used in various fields such as automobiles, locomotive manufacturing, hardware products, electronics, electrical appliances, instruments, cables, kitchenware, furniture, environmental protection, lighting, toys, etc. Its role is reflected in the following aspects:
- Punching machines can process various forms of metal parts, such as phone casings, battery cells, LCD modules, etc.
- Punching machines can be used for stretching and cold stamping, and are used for manufacturing complex shapes such as car bodies, sheet metal, bumpers, and wheel hubs.
- Punching machines can perform cutting and are used to manufacture various specifications of metal plates and films.
Punching Machine Introduction: Working Flow
The stamping process involves multiple steps, including cutting, punching, bending, and forming. During the punching process, the sheet punch machine cuts the desired shape from the metal plate. Perforation forms holes or grooves in metal, while bending and shaping the metal into the desired structure. For example, in the production of car body panels, stamping machines accurately form complex curves and contours from metal.
Processing Method Of Punch Machine
- Single punch: Single completion punching, including straight line spreading, arc spreading, circular spreading, and punching of grid holes.
- Continuous punching in the same direction: The method of stacking rectangular molds can be used to process long holes, cut edges, etc.
- Continuous punching in multiple directions: The method of using small molds to process large holes.
- Eating away: The processing method of using a small circular die to continuously punch arcs with a smaller step distance.
- Single forming: The processing method of one-time shallow stretching forming according to the shape of the mold.
- Continuous forming: Forming processing methods with larger dimensions than molds, such as large-scale louvers, rolling ribs, rolling steps, and other processing methods.
- Array Forming: Processing multiple identical or different workpieces on a large board using different processing methods.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Punching machines have many advantages in metal processing.
- Firstly, punching machines use molds for processing, which can quickly and efficiently mass produce parts with the same shape, improving production efficiency.
- Secondly, keeping the punchingtemperature of the metal sheet low during punching is beneficial for maintaining the mechanical properties and surface quality of the material.
- In addition, punch machineshave high machining accuracy and consistency, which can meet the machining needs of components with high requirements for size and shape.
- Last but not least, punching machinecan also process metal sheets of various materials, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, etc., with high adaptability.
However, punch presses also have some limitations and challenges.
- Firstly, the manufacturing cost of punch molds is relatively high, requiring certain design and manufacturing capabilities.
- Secondly, punching machines have high requirements for materials, and the toughness and plasticity of the materials determine whether the punching machine can successfully process them.
- In addition, during the punching process, the material will experience a certain degree of stress and deformation, so it is necessary to strictly inspect and maintain the mold and punching machine to ensure processing quality.
- Finally, the processing speed of punching machineis fast, which requires high technical requirements for operators and certain operational skills.

Punching Machine Classification
Divided By Different Driving Forces:
Mechanical Punching Machine
Mechanical punching machines use mechanical power (usually driven by a crankshaft) to perform stamping operations. They are suitable for medium speed applications and widely used in automotive and home appliance manufacturing. Mechanical punch machines are renowned for their sturdy structure and reliability, making them an ideal choice for mass production of simple metal parts.
Hydraulic Punching Machine
Hydraulic punching machines use hydraulic power to drive stamping actions, providing higher force capabilities for heavy-duty applications. They are very suitable for stamping thick materials and forming complex shapes. Hydraulic punching machines are commonly used in the aerospace and construction industries to produce structural components and parts that require deep drawing.
Pneumatic Punching Machine
Pneumatic punching machines use compressed air to provide power for stamping actions, making them suitable for lightweight operations and delicate materials. They are commonly used in the electronics and jewelry industries, where precise and gentle handling of materials is crucial. Pneumatic stamping machines are the preferred choice for tasks such as embossing and engraving.
Servo Punching Machine
Servo punching machine uses servo motors to precisely control the stamping process, achieving higher precision, energy efficiency, and versatility when handling complex tasks. Servo driven punching machines provide greater flexibility in adjusting stroke length, stamping speed, and dwell time, making them an ideal choice for manufacturing customized parts with strict tolerances.
Progressive Punching Machine
Progressive punching machines perform multiple stamping operations in one pass, enabling efficient mass production of complex parts with minimal manual operation. The metal strip is continuously fed into a series of molds, and each workstation performs different operations such as perforation, bending, and forming. Progressive punching machines are widely used in the automotive and home appliance industries for producing components such as brackets, clips, and connectors.
Classified By Slider Movement Mode
According to the movement mode of the slider, there are three types of punch presses: single action, compound action, and triple action. However, the most commonly used single action punch press today is a slider. Compound action and triple action punch presses are mainly used for the extension processing of automobile bodies and large machined parts, and their quantities are very small.
Classified By Machine Structure
According to the different machine structures, punching machine can be classified into two categories: back mounted (C-type) and straight column (H-type). The C-type punching machine generally has a nominal pressure of less than 300T based on its body characteristics (front opening), and the operating pressure is generally around 50% of the nominal pressure. The H-type punching machine has a symmetrical body and can withstand eccentric loads during operation. The nominal pressure is generally above 300T.
Classified By Slider Drive Mechanism
Crankshaft Punching Machine
A punch press that uses a crankshaft mechanism is called a crankshaft punching machine.
Use this institution. The reason for using the crankshaft mechanism the most is that it is easy to manufacture, can correctly determine the lower end position of the stroke, and the slider activity curve is basically practical for various machining. Therefore, this type of punching is widely used for punching, bending, stretching, hot forging, warm forging, cold forging, and almost all other punching processes.
Crankless Punching Machine
Non crankshaft punch press, also known as eccentric gear punch machine, eccentric gear punch press. The eccentric gear punch press structure has better shaft rigidity, lubrication, appearance, and maintenance than the crankshaft structure, but the disadvantage is that it is more expensive. When the stroke is long, the eccentric gear punch is more advantageous, while when the stroke of the dedicated punching machine is short, the crankshaft punch is better. Therefore, small-sized machines and high-speed punching machines are also in the field of crankshaft punch.
Knuckle Punching Machine
The use of knuckle mechanism on slider drive is called knuckle punching machine. This punch has a unique slider activity curve where the slider speed near the bottom dead center becomes extremely slow (measured by the crankshaft punch). And it also correctly determines the dead center position below the stroke, therefore, this punch press is suitable for compression processing such as embossing and finishing, and is most commonly used in cold forging today.
Friction Punching Machine
The punching machine that uses friction transmission and spiral mechanism on the track drive is called a friction punch press. This type of punch machine is most suitable for forging and crushing operations, and can also be used for bending, forming, stretching, and other processing. It has versatile functions and was widely used before the war due to its low price. Due to the inability to determine the lower end position of the stroke, poor machining accuracy, slow production speed, overload caused by control operation errors, and the need for skilled technical skills, it is gradually being phased out today.
Screw Punching Machine
The use of a screw mechanism on the slider drive mechanism is called a screw punching machine (or screw punch press).
Rack Punching Machine
The use of a rack and pinion mechanism on the slider drive mechanism is called a rack and pinion punch machine. Spiral punch press and rack punch press have almost identical characteristics, and their features are roughly equivalent to those of hydraulic punch press. Previously used for pressing liners, debris, and other items, such as squeezing, pressing oil, bundling, and pressing shell casings (hot thinning processing), but now it has been replaced by hydraulic punching machines and is no longer used except in extremely special circumstances.
Link Punching Machine
The punch press that uses various linkage mechanisms on the slider drive mechanism is called a linkage punching machine. The purpose of using a connecting rod mechanism is to maintain the stretching speed within the limit while reducing the processing cycle during the stretching process. By reducing the speed change of the stretching process, the speed of the approach stroke from the top dead center to the starting point of the processing and the return stroke from the bottom dead center to the top dead center can be accelerated, making it have a shorter cycle than the crankshaft punch to improve productivity. This type of punch machine has been used since ancient times for deep drawing of cylindrical containers with narrow bed surfaces, and has been used for processing automotive body panels with wider bed surfaces.
Cam Punching Machine
The punch press that uses a cam mechanism on the slider drive mechanism is called a cam punch machine. The characteristic of this punching machine is to have a properly crafted cam shape in order to easily obtain the desired slider movement curve. However, due to the nature of the cam mechanism, it is difficult to convey large forces, so the punching capacity of this punch is very small.
Structural Composition Of Punching Machine

The punch press is mainly composed of the following parts:
- Machine body: composed of machine base, column, mechanical arm, hydraulic mechanical cylinder, etc. Among them, the frame serves as the structure that supports and fixes the entire punch press, with high stability and rigidity.The slider is the main component for the up and down movement of the punch press, which is connected to the frame through sliding or rolling connections.The bed is a workbench for placing workpieces, with a flat and sturdy surface, used to ensure stability during the up and down movement of the punch press
- Transmission mechanism: mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic and other transmission methods are used to transmit the driving force to the working part. The driving device usually consists of an electric motor, a reducer, a clutch, and a gear mechanism, used to provide the power and force required for the movement of the punch press
- Working position: mainly composed of punch, guide column, pull rod, etc.
- Control system: Control the operation, stopping, and automatic adjustment of equipment through electrical or hydraulic means. The control system consists of electrical components, hydraulic components, and computers, which are used to control and monitor various operating parameters of the punching machine to ensure the accuracy and stability of the punching process.
Punching Machine Introduction: Terminology
- Mold: A specialized tool used in punching machines for forming and cutting metal parts.
- Punch head: A part of a punching machine that applies force to a metal plate or coil to form the desired shape.
- Punching: The process of cutting a flat shape from a metal plate, leaving behind the required components.
- Perforation: Using a punch and mold to punch or open holes in a metal plate.
- Forming: Using specialized molds to bend or shape metal into the desired structure.
- Embossing: Using convex and concave molds to create raised indentations or patterns on metal surfaces.
- Embossing: Creating complex patterns or textures on a metal surface.
- Tonnage: The maximum force that a stamping machine can apply, usually measured in tons.
- Stroke length: The distance traveled by the punch during the stamping process.
- Speed: The rate at which a stamping machine performs operations, measured in strokes per minute.
- Mold pad: A component that supports the blank during the molding process to minimize wrinkles and control material flow.
- Quick mold change system: a mechanism that allows for quick and efficient mold replacement, reducing downtime between different production runs.
- Automation: Integration of robotic systems and computer control to optimize production processes and minimize human intervention.
- CNC (Computer Numerical Control): A computerized system that can automatically control stamping machines to achieve precise and repeatable operations.
How To Purchase A Punching Machine

Choosing the appropriate punching machine manufacturer is crucial for meeting specific production requirements. Factors to consider include the manufacturer’s experience, professional knowledge, and ability to provide customized solutions. A reputable manufacturer should provide excellent customer support, including training, technical assistance, and timely maintenance services, to ensure smooth operation and maximize machine uptime.
Key Factors When Purchasing A Punching Machine
Before investing in stamping machines, sheet metal forming manufacturers should evaluate punching machine factories’ production capacity, material types, and part complexity. The selected machine should have the required tonnage, bed size, and speed to meet production needs. Compatibility with different mold configurations and tool options is crucial for meeting the multi-functionality of different manufacturing needs.
Speed
There are two speeds of punching machines on the market called high speed punching machine, one is high speed 400 times/minute, and the other is 1000 times/minute. If your product requires a mold speed of 300 times/minute or higher, you should choose a punch press with 1000 times/minute. Because the equipment cannot be used to the extreme, and punching machines with a speed of less than 400 times per minute generally do not have a mandatory lubrication system. Only butter lubrication is used in the joint parts, and the punch structure adopts a slider type, which makes accuracy difficult to guarantee. Over long periods of work, it wears out quickly, accuracy decreases, molds are easily damaged, and the machine and mold maintenance rate is high, which delays time and affects delivery time.
There are two speeds of punching machines on the market called high speed punching machine, one is high speed 400 times/minute, and the other is 1000 times/minute. If your product requires a mold speed of 300 times/minute or higher, you should choose a punch press with 1000 times/minute. Because the equipment cannot be used to the extreme, and punching machines with a speed of less than 400 times per minute generally do not have a mandatory lubrication system. Only butter lubrication is used in the joint parts, and the punch structure adopts a slider type, which makes accuracy difficult to guarantee. Over long periods of work, it wears out quickly, accuracy decreases, molds are easily damaged, and the machine and mold maintenance rate is high, which delays time and affects delivery time.
Accuracy
The precision of the punching machine is mainly manifested as:
- Parallelism
- Verticality
- Total gap
High precision punching machines can not only produce good products, but also cause less damage to molds, saving not only mold maintenance time but also maintenance costs.
- There are many things processed by punching machines, which can be divided into four categories: cutting, drawing, forming, stamping, etc. It can also be further subdivided into four categories: blank making, punching, cutting, drawing, bending, forming, stamping, etc.
- The tonnage of a punch press is estimated based on the total tonnage required for mold processing. Therefore, the main factors affecting the tonnage of a punch press include the length of the part perimeter, material thickness, material strength, and other characteristics.
- The length of the journey and the area of the workbench are determined by the size and depth of the stamped parts.
- The daily output is mainly used to calculate the number of strokes per minute of the punching machine and the required number of punching machines. The choice of high-speed or low-speed punching machines is determined to meet the overall production needs.
Therefore, the various characteristics are considered together, including part processing characteristics, material characteristics, tool usage characteristics, etc. Generally speaking, for processes such as embryo punching and perforation, short stroke high-speed punching machines are required; For processes such as molding and drawing, long stroke and slower speed punching machines are required; When used in processes such as embossing and embossing, a short stroke punch with high energy at the bottom dead center must be used.
In addition, for the forming, drawing, and pressing processes, there is a critical pressing rate depending on the material used. Therefore, the selection of materials also needs to be coordinated with the manufacturing process. In order to achieve the quality characteristics of the product, the accuracy of the punching machine must also be considered in order to manufacture excellent products.
Conclusion
Punching machines are indispensable tools in the metal processing industry, providing multifunctional and efficient solutions for the forming and shaping of metal components. Each type of plate punching machine can meet specific production needs, from high-speed mass production to complex customized parts. The continuous development of stamping technology, including servo drive and progressive machines, has completely changed the metal processing industry, enabling manufacturers to meet the needs of modern manufacturing and provide high-quality products in various fields. By read this punching machine introduction guide, users can understand the different types and processes of punching machines, optimize their production capacity and maintain competitiveness in today’s dynamic market.
Related Articles: