Table of Contents
What is CO2 laser cutting machine? CO2 laser cutting machine is a device that uses an infrared laser beam (usually with a wavelength of 10.6μm) generated by a CO2 laser to cut, engrave or mark various materials. It is widely used in the processing of materials such as metal, plastic, wood, leather, cloth, glass and acrylic.
1. What is CO2 laser cutting machine?
A CO2 laser cutting machine is a device that uses a high-energy infrared laser (wavelength of about 10.6μm) generated by a CO2 laser to cut, engrave or mark materials. It belongs to thermal processing technology and is widely used in precision processing of non-metallic materials (such as wood, acrylic, plastic, cloth, leather, etc.) and some metal materials.
2. Working principle of CO2 laser cutting machine

CO2 laser cutting machine is a kind of equipment that uses high-energy infrared laser (wavelength of about 10.6μm) generated by CO2 laser to heat, melt or gasify materials, and blows away slag through auxiliary gas to achieve high-precision cutting. How CO₂ laser cutting works?
Working process
1) Laser generates CO2 laser beam
Using CO2 gas mixture (main components: carbon dioxide, nitrogen, helium) as the working medium, CO2 molecules are excited under the action of high-voltage electric field to release infrared laser beam with specific wavelength (10.6μm).
This laser beam has high energy density and good monochromaticity, which is suitable for cutting non-metallic materials and some metal materials.
2) Optical system transmission and focusing
The laser beam is guided to the cutting head through a reflector and focusing lens, and focused into a very small diameter spot (usually less than 0.2mm).
The high energy of the laser instantly heats the material at the spot to a molten or gasified state.
3) The material is heated, melted or vaporized
After the focused laser beam is irradiated onto the surface of the material, the material absorbs the laser energy and its temperature rises rapidly.
Reactions of different materials:
- Fusible materials (such as plastics and acrylics): directly melt and blow away.
- Combustible materials (such as wood and leather): carbonize and evaporate.
- Metallic materials: require high-power lasers and are assisted by oxygen for oxidation combustion to enhance cutting efficiency.
4) Auxiliary gas blows away slag
During the cutting process, high-pressure auxiliary gases (such as oxygen, nitrogen or air) are usually used:
- Oxygen (O₂): provides combustion assistance to improve metal cutting efficiency.
- Nitrogen (N₂): suitable for materials that require high-quality cutting edges (such as stainless steel).
- Compressed air: an economical solution suitable for low-cost processing.
High-speed airflow can cool the cutting area, prevent overburning of the edge, and blow away the molten material to improve cutting quality.
5) CNC system accurately controls cutting path
The computer numerical control (CNC) system or laser control software presets the cutting path and controls the laser head to move according to the specified pattern.
Main methods of CO₂ laser cutting
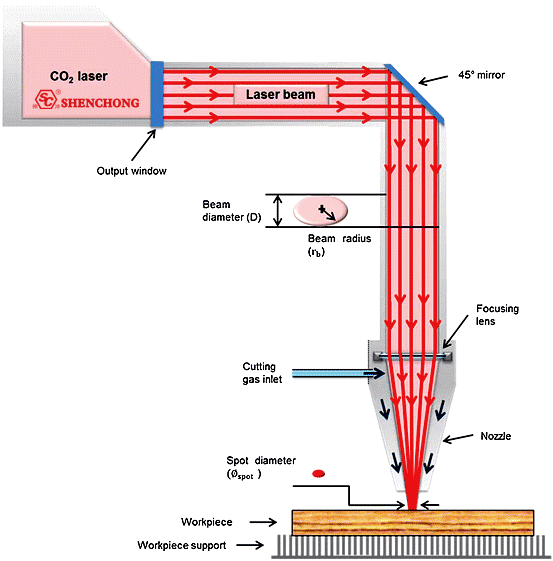
Carbon dioxide laser cutting is mainly based on the absorption characteristics of materials to laser energy, combined with different physical and chemical reactions to achieve efficient processing. Common cutting methods include vaporization cutting, melting cutting, oxidation cutting and dicing cutting.
1) Vaporization Cutting
Principle:
- The laser beam heats the surface of the material to the boiling point in a very short time, causing it to vaporize (sublimate) directly.
- Since there is no melting stage, the material directly turns into steam and is carried away by high-speed auxiliary gas.
Features:
- Suitable for materials with high melting point and low thermal conductivity.
- The incision is extremely narrow and the edges are neat.
- Extremely high laser power is required (generally higher than melting cutting).
Applicable materials:
- Wood
- Paper
- Plastic (partial)
- Acrylic
- Composite materials
- Some ceramic materials
2) Fusion Cutting
Principle:
- The laser beam heats the material to the melting point to melt it.
- High-pressure inert gas (such as nitrogen N₂, argon Ar) blows away the molten material without oxidation reaction.
Features:
- Applicable to materials that do not want to oxidize, such as stainless steel, aluminum, etc.
- The cutting surface is smooth and has no oxide layer.
- Auxiliary gas with higher air pressure is required to blow away the molten material.
Applicable materials:
- Stainless steel
- Aluminum and aluminum alloys
- Titanium and titanium alloys
- Some plastics
3) Flame Cutting / Oxidation Cutting
Principle:
- Using oxygen (O₂) as auxiliary gas, the laser beam heats the metal to the ignition point, causing it to undergo a violent oxidation reaction with oxygen, generating a large amount of heat energy and accelerating the cutting process.
- The oxide slag generated by the reaction is blown away by the high-speed airflow to form a cutting seam.
Features:
- The cutting speed is faster than melting cutting (because the oxidation reaction generates additional heat).
- Applicable to oxidizable materials such as carbon steel, but an oxide layer will be formed (post-processing is required).
- Applicable to cutting thicker metal materials.
Applicable materials:
- Carbon steel
- Low alloy steel
- Some cast irons
4) Scribing / Controlled Fracture Cutting
Principle:
- Use low-power laser to scratch a microcrack on the surface of brittle materials, and then apply mechanical or thermal stress to make the material break along the crack.
Features:
- Applicable to fragile materials such as glass and ceramics to avoid direct melting or gasification.
- The cutting edge is neat and the heat affected zone (HAZ) is reduced.
- The laser power and focus need to be precisely controlled to avoid uneven material fracture.
Applicable materials:
- Glass (such as optical glass, quartz glass)
- Ceramics
- Artificial sapphire
Comparison table of various cutting methods:
Cutting method | Heat affected zone | Cutting speed | Cut surface quality | Applicable materials |
Vaporization cutting | Small | Moderate | Very smooth | Wood, paper, plastic, acrylic |
Melt cutting | Low | Moderate | High (no oxide layer) | Stainless steel, aluminum, titanium |
Oxidation cutting | High | Fast | Low (need to remove oxide layer) | Carbon steel, low alloy steel |
Scribing cutting | Very small | Fast | Very high (no melt) | Glass, ceramics |
Characteristics of CO₂ laser cutting and applicable materials table:
Cutting method | Features | Applicable materials |
Vaporization cutting | High-energy laser directly vaporizes the material | Wood, plastic, acrylic, paper |
Melt cutting | Material melts, assisted by gas blowing to remove slag | Metal, stainless steel, plastic |
Oxidation cutting | Relies on oxygen to assist combustion, speeding up metal cutting | Carbon steel, alloy steel |
Scribing cutting | Low-power laser is used for cutting brittle materials | Glass, ceramics |
Summary:
- Vaporization cutting: suitable for low melting point materials (wood, plastic) and applications requiring high precision cutting.
- Melt cutting: suitable for cutting metals such as stainless steel and aluminum that require non-oxidized edges.
- Oxidation cutting: suitable for metal processing such as carbon steel that requires efficient cutting but allows an oxide layer.
- Scribing cutting: suitable for fine processing of brittle materials such as glass and ceramics.
3. What is CO2 laser cutting machine feature?

CO₂ laser cutting machine is a non-contact thermal processing equipment, which mainly uses infrared laser with a wavelength of 10.6μm for high-precision cutting and engraving, and is suitable for a variety of non-metallic materials and some metal materials. The following are its main features:
1) Wide range of applicable materials
Applicable to non-metallic materials: such as wood, acrylic, plastic, leather, cloth, rubber, paper, glass, ceramics, etc.
Can process some metals: Thin metals (such as stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum alloy) can be cut with the addition of auxiliary gas (such as oxygen) or special coating.
Friendly to organic materials: Laser cutting does not produce physical stress and is not easy to cause material damage.
2) High cutting accuracy
The accuracy can reach ±0.1mm, which is suitable for fine engraving and complex pattern cutting.
The spot diameter is small and the heat-affected zone is small, which reduces cutting deformation and burning.
No mold is required, CAD/CAM design is supported, and high-precision automatic processing is achieved.
3) Good cutting quality and smooth edges
The high-energy laser beam melts the material, and the cutting edge is neat, without secondary grinding.
The cut is smooth, burr-free, and mechanically deform-free, which improves product quality.
Suitable for high-demand processing in industries such as advertising, decoration, packaging, and clothing.
4) High efficiency & automation
The cutting speed is fast, more efficient than traditional tool cutting, and suitable for mass production.
Supports CNC numerical control system, which can automatically program and optimize cutting paths to improve production efficiency.
Can directly import design files such as CAD and CorelDRAW to achieve intelligent operation.
5) Non-contact processing, low loss
Laser cutting is non-contact processing, which does not exert mechanical pressure on the material and is not easy to cause damage.
No tool wear, reduced replacement of mechanical parts, and reduced maintenance costs.
Suitable for fragile, soft or delicate materials (such as glass, cloth, acrylic, etc.).
6) Environmental protection & low pollution
No dust, no scraps, no noise, cleaner than traditional cutting methods.
Smoke exhaust equipment can be used during laser cutting to reduce the impact of smoke on the environment.
Avoids waste generated during mechanical cutting and improves material utilization.
7) Engravable & Marking
In addition to cutting, laser engraving can also be performed, which can achieve fine pattern engraving and personalized customization.
Suitable for application scenarios such as advertising production, gift engraving, and electronic component marking.
8) Integrable automation system
Can be combined with industrial equipment such as assembly lines, robots, CNC, etc. to improve the level of production automation.
Suitable for mass production and intelligent manufacturing, improving efficiency and reducing labor costs.
4. The difference between CO₂ laser cutting machine and fiber laser cutting machine
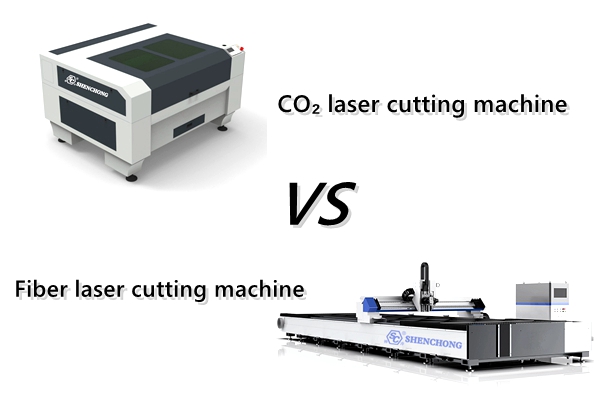
Features | CO₂ laser cutting machine | |
Applicable materials | Mainly used for non-metal, can cut thin metal | Mainly used for metal cutting |
Wavelength | 10.6μm (suitable for non-metal) | 1.06μm (suitable for metal) |
Cutting quality | Smooth cut, suitable for fine engraving | Higher metal cutting efficiency |
Equipment cost | Relatively low | Higher price, low maintenance cost |
Energy consumption | Relatively high | More energy-efficient |
Application areas | Widely used in advertising, clothing, packaging, woodworking, etc. | Mainly used in metal processing, automobile, aviation and other industries |
5. Summary
What is CO2 laser cutting machine? A CO₂ laser cutting machine is a type of laser cutter that uses a carbon dioxide (CO₂) laser to cut, engrave, or mark various materials. It is one of the most commonly used laser cutting technologies due to its precision, efficiency, and versatility.
Advantages of CO2 Laser Cutting:
- High cutting precision
- Smooth and clean edges
- Works with a wide range of non-metallic materials
- Fast processing speeds
- Low maintenance compared to mechanical cutting
Disadvantages:
- Not ideal for cutting thick or reflective metals
- Requires regular maintenance (e.g., cleaning lenses, replacingCO2 laser tubes)
- Higher energy consumption compared to fiber lasers
Why choose CO₂ laser cutting machine?
- Suitable for non-metal cutting, such as wood, plastic, acrylic, leather, cloth, etc.
- High cutting accuracy, suitable for advertising, packaging, decoration, industrial manufacturing and other industries.
- Non-contact processing, low loss, no need to change tools, low maintenance cost.
- Environmentally friendly and pollution-free, reducing dust, noise and material waste.
- Support automation, can integrate intelligent production system to improve production efficiency.